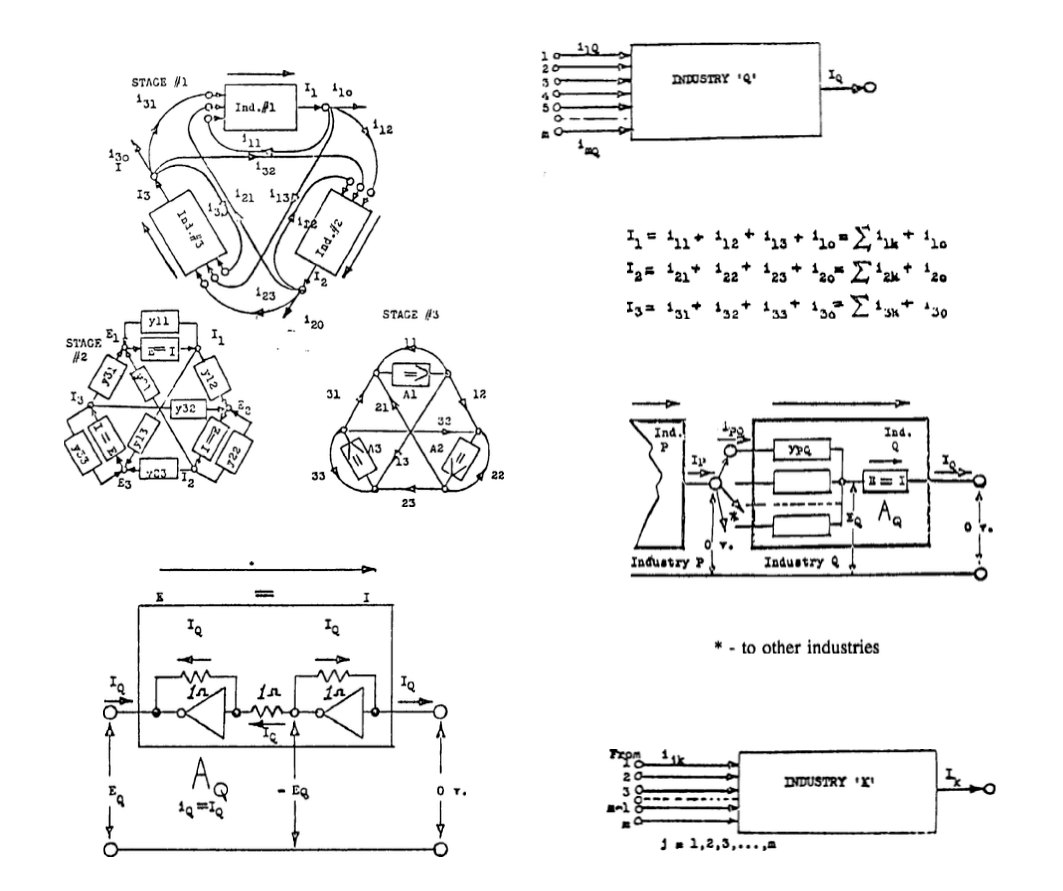
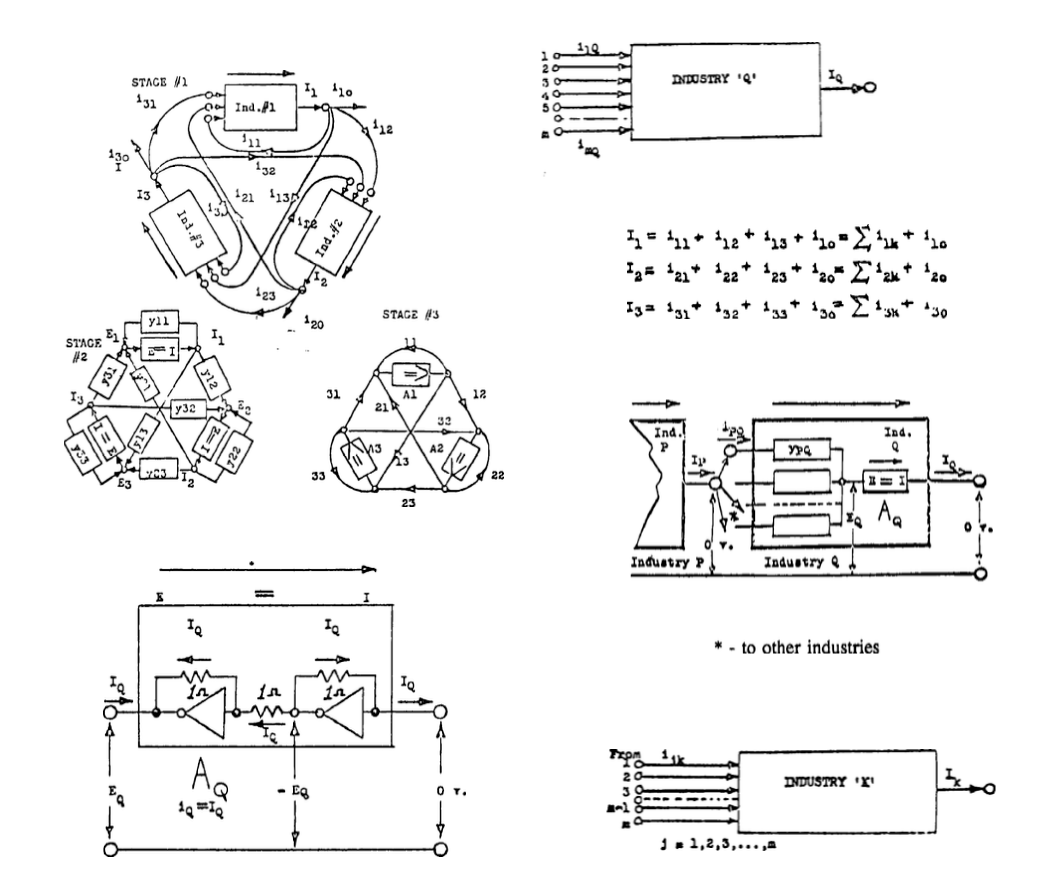
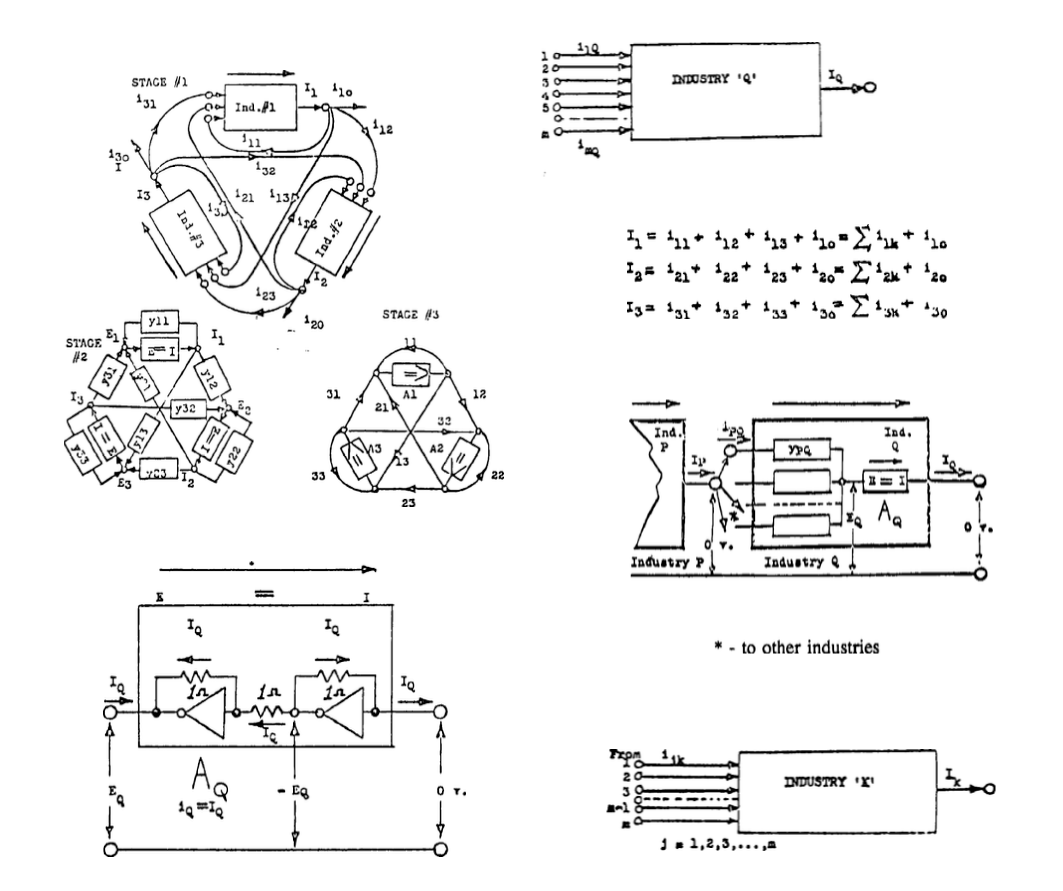
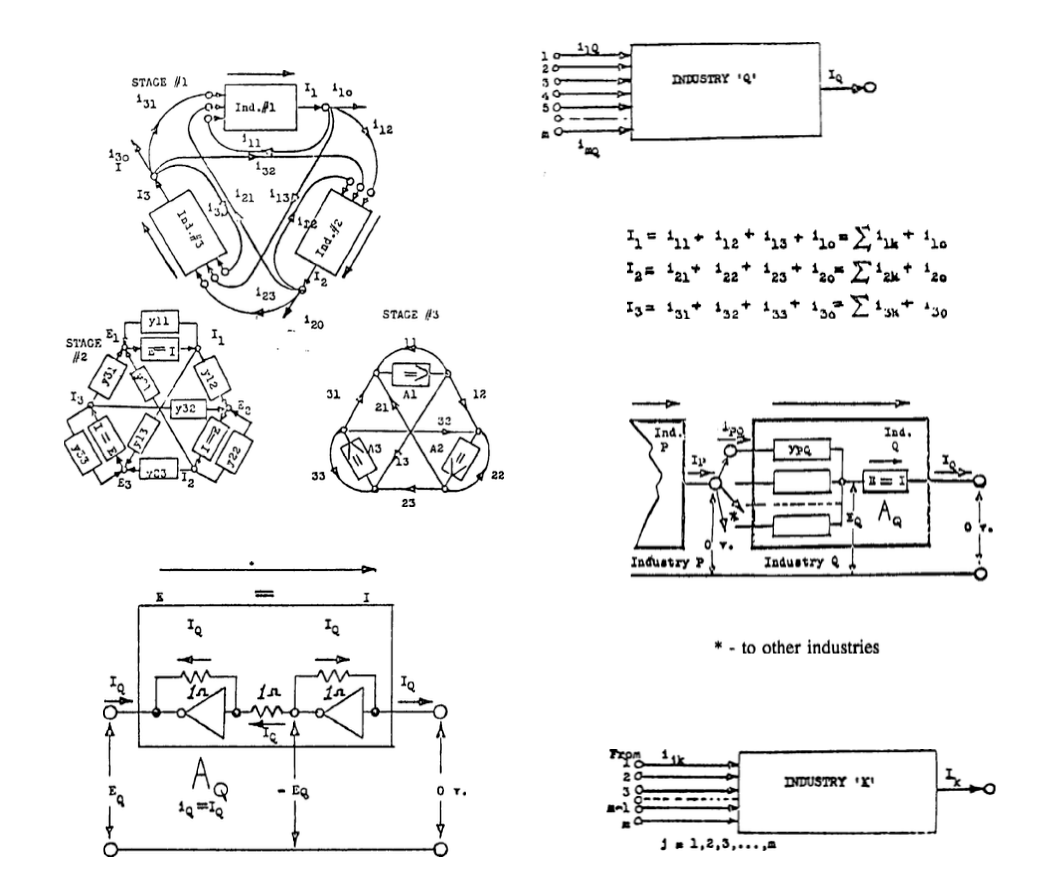
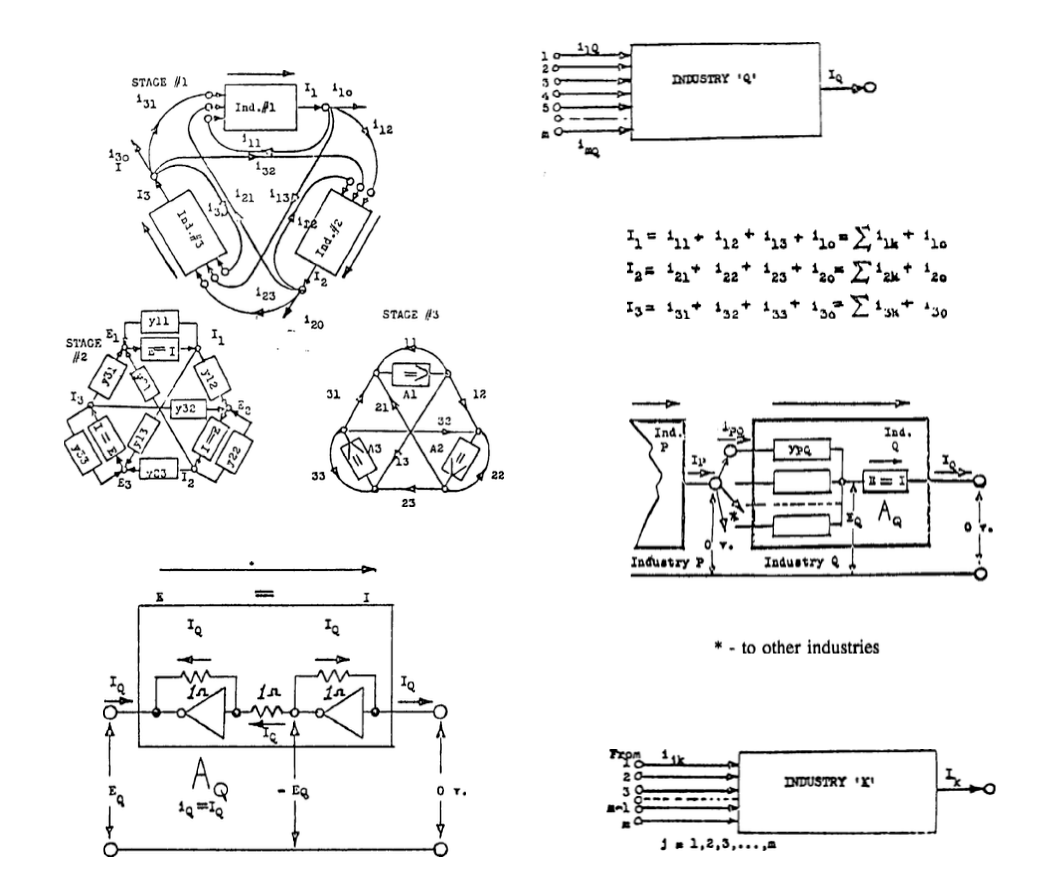
Three Industrial Classes
Industries fall into three categories or classes by type of output:
- Class #1 - Capital (resources)
- Class #2 - Goods (commodities or use - dissipative)
- Class #3 - Services (action of population)
- Class #1 industries exist at three levels:
- Nature - sources of energy and raw materials.
- Government - printing of currency equal to the gross national product (GNP), and extension of currency in excess of GNP.
- Banking - loaning of money for interest, and extension (inflation/counterfeiting) of economic value through the deposit loan accounts.
- Class #2 industries exist as producers of tangible or consumer (dissipated) products. This sort of activity is usually recognized and labeled by the public as "industry."
- Class #3 industries are those which have service rather than a tangible product as their output. These industries are called (1) households, and (2) governments. Their output is human activity of a mechanical sort, and their basis is population.